Singapore Social Media Landscape in 2025: Trends and Opportunities (Updated October 2025)
Singapore, with its population of 6.11 million (as of June 2025) and aspiring to be a global Smart Nation, exhibits a dynamic digital environment characterized by substantial growth and increasing integration of technology into everyday life and business operations. With 95.8% internet penetration and 179% mobile penetration—among the world’s highest rates—understanding the nuances of this digital landscape, particularly the evolving social media sphere, is crucial for businesses seeking success in Singapore.
Singapore’s social media ecosystem is evolving at breakneck speed, driven by technological innovation, changing consumer behaviors, and the city-state’s position as Southeast Asia’s digital hub. As we navigate through 2025, understanding these dynamics is crucial for businesses, marketers, and content creators looking to succeed in the Lion City’s competitive digital landscape.
Singapore’s digital economy is a significant and mature component of the thriving Southeast Asian region. With 6.11 million residents (4.20 million citizens and permanent residents, plus 1.91 million non-residents), Singapore demonstrates high per capita digital spending and acts as a vital hub for regional headquarters and investment. The nation boasts 5.61 million internet users (95.8% penetration) and 10.5 million mobile connections (179% penetration), making it one of the world’s most connected societies. Singapore’s commitment to digital advancement is reinforced by strategic initiatives such as the “Infocomm Media 2025” plan and the “Smart Nation 2.0” strategy, which emphasize data utilization, trust, and seamless integration of technology. Singapore became the world’s first country to achieve nationwide 5G coverage, further cementing its position as Southeast Asia’s digital hub. These initiatives provide important context for understanding the specific dynamics of social media adoption and usage within Singapore.
Current State of Social Media Singapore: By the Numbers
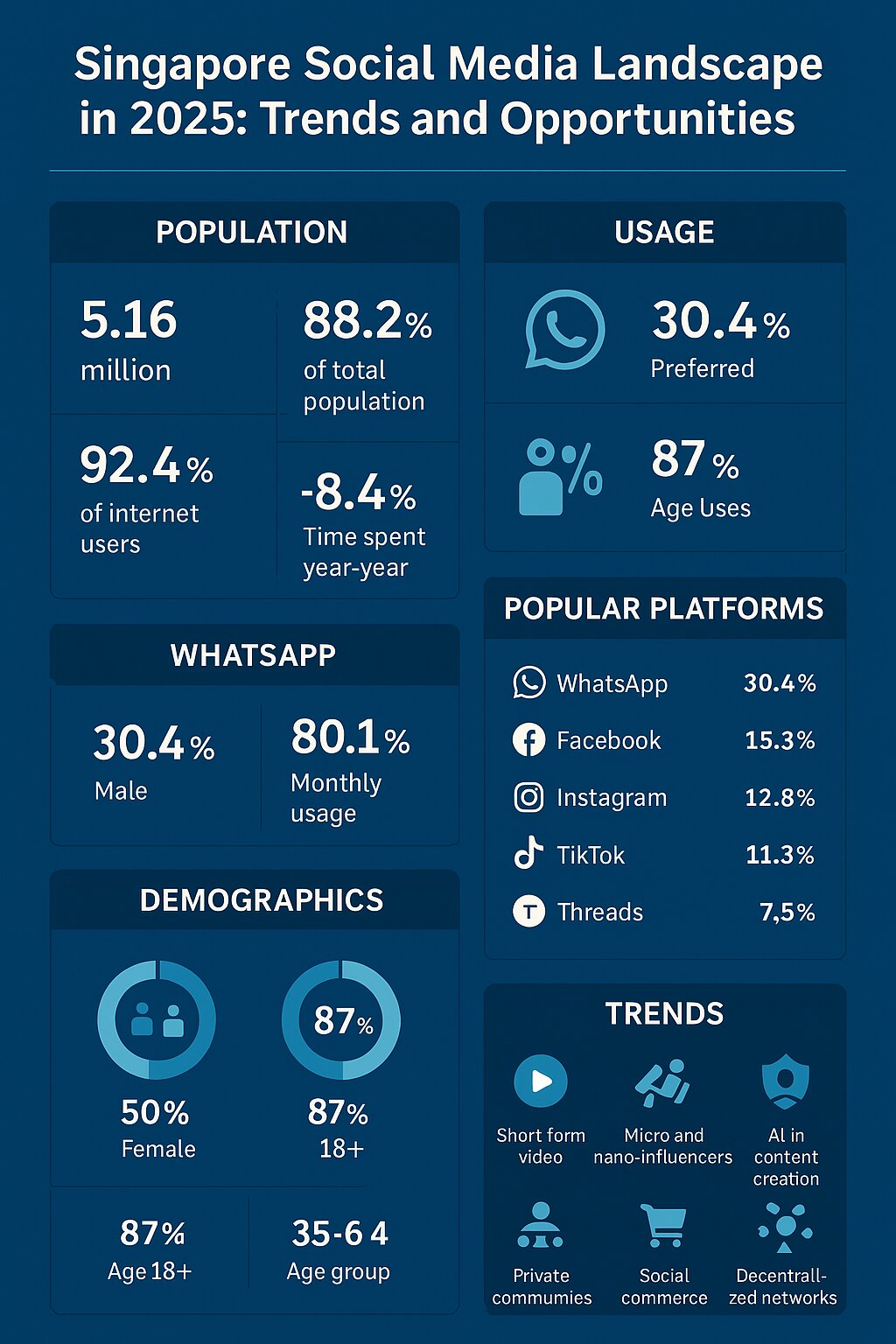
In early 2025, Singapore showcased a highly connected society, with a substantial majority of its population actively engaged on social media. The number of social media user identities reached 5.16 million, representing 88.2% of the total population (6.11 million) and 92.4% of internet users (5.61 million). This highlights a mature market where social media is deeply embedded in the daily digital habits of Singaporeans, with 97% of social media access happening via mobile devices. Despite this widespread adoption, the average time spent on social media was 2 hours and 39 minutes per day, with users accessing an average of 7.2 different platforms per month. This suggests users are spreading their time across a wider array of platforms while engaging deeply with video-centric platforms like TikTok and YouTube.
Platform Dominance in Singapore 2025
WhatsApp emerged as the most preferred social media platform in Singapore, favored by 30.4% of users and used monthly by 80.1% of the population.
WhatsApp continues to reign supreme with 89% penetration, serving as the primary communication tool for both personal and business interactions. The platform’s integration with Meta’s business suite has transformed it into a powerful e-commerce channel, with local businesses reporting 40% of customer inquiries coming through WhatsApp Business.
Facebook remained a strong second, with a 15.3% preference rate and 71.9% monthly usage. TikTok commanded significant user attention, with 3.63 million users aged 18+ in Singapore and users spending an average of 34 hours and 29 minutes per month on the platform. TikTok has emerged as the fastest-growing platform, with 56.6% usage rate and adding 251,000 users (+7.4%) year-over-year, making it the go-to platform for discovering new brands, restaurants, and trends. Its algorithm’s preference for local content has made it indispensable for Singapore-based businesses.
YouTube also held a prominent role, reaching 88.2% of the population with its advertisements and maintaining a user base of 5.16 million. Although globally popular, Instagram showed lower preference levels in Singapore compared to WhatsApp and Facebook.
Instagram maintains its position as the visual storytelling champion, with 3.15 million users in Singapore and 62.6% usage rate. Instagram’s ad reach is equivalent to 53.8% of the total population. The introduction of Instagram Threads has created new opportunities for real-time engagement, particularly among younger demographics aged 18-34.
Newer platforms like Meta’s Threads gained momentum quickly, ranking second among the most downloaded mobile apps. In terms of general usage, messaging apps and social networks remained the top categories, accessed by 97% and 95.9% of internet users respectively.
Demographics and User Behavior
The demographic breakdown of social media users in 2025 revealed a nearly even gender split, with 50% female and 50% male users. About 87% of accounts were held by users aged 18 and above, with the 25–34 age group representing the largest segment at 35.6%. Platform-specific analytics showed nuanced gender differences: Facebook had 48% female and 51.5% male users; YouTube had 47% female and 53% male; Instagram had 54.2% female and 45.8% male; TikTok had 54% female and 46% male; and LinkedIn had 46.2% female and 53.8% male. The majority of social media users in Singapore were aged between 18 and 44, indicating a youthful, digitally engaged population.
Singaporeans spent an average of 2 hours and 39 minutes daily on social media, with TikTok standing out as the platform with the highest engagement time—34 hours and 29 minutes per month—followed by YouTube at 29 hours and 45 minutes. This highlights TikTok’s and YouTube’s dominance in capturing and holding user attention through video content. The widespread use of multiple platforms (7.2 on average) suggests Singaporeans are platform-hopping to consume different types of content, from quick entertainment on TikTok to professional networking on LinkedIn and business communication on WhatsApp.
Emerging Trends Shaping Singapore’s Social Media Future
A number of key trends shaped the social media landscape in 2025. Short-form video content continued to dominate, with TikTok, Instagram Reels, and YouTube Shorts proving highly engaging. Micro and nano-influencers gained traction as brands leaned into more authentic, niche community engagement. Collaborating with a trusted Influencer Marketing Agency became increasingly valuable for brands aiming to identify and activate high-impact creators at scale.
AI-Powered Content Creation Revolution Singapore’s tech-savvy population has embraced AI tools for content creation faster than most markets. Local businesses are leveraging AI for multilingual content creation, essential in Singapore’s diverse linguistic landscape. Tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney are being used to create content in English, Mandarin, Malay, and Tamil, addressing Singapore’s multicultural audience effectively.
Impact for Marketers: Brands that invest in AI-powered content strategies are seeing 60% faster content production cycles and 35% better engagement rates across local campaigns.
Artificial intelligence played a larger role in content creation and personalisation, helping brands better tailor their messaging. Employee-generated content emerged as a trustworthy and relatable branding tool. There was a shift toward private groups and communities, reflecting users’ preference for more intimate online spaces.
Hyper-Local Community Building The concept of “digital kampongs” is gaining traction, where social media platforms are being used to build hyper-local communities around specific neighborhoods, interests, or cultural groups. Facebook Groups dedicated to specific HDB estates, condo communities, and local interest groups have become powerful marketing channels.
Success Strategy: Brands are partnering with local community leaders and micro-influencers to create authentic connections within these digital neighborhoods.
Social commerce also expanded rapidly, with integrated shopping features allowing seamless purchases directly on platforms. Social Commerce Integration Singapore’s e-commerce landscape is increasingly social-first. Instagram Shopping, Facebook Marketplace, and TikTok Shop have become primary discovery channels for local businesses. The government’s support for digital payment systems like PayNow and GrabPay has made social commerce transactions seamless.
Key Metrics: – 73% of Singapore consumers have made purchases directly through social media platforms – Average order value through social commerce: S$127 – Social media influences 89% of purchase decisions among millennials and Gen Z – Mobile devices account for 78.13% of all B2C e-commerce transactions – 70.1% of Singapore’s consumer e-commerce transactions happen on mobile devices
Sustainability and Social Responsibility Content Singapore’s commitment to becoming a “City in a Garden” and achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 has influenced social media content trends. Brands showcasing genuine sustainability efforts and corporate social responsibility are seeing significantly higher engagement rates.
Trending Topics: – Zero-waste lifestyle content – Local food sustainability – Green technology adoption – Community volunteer initiatives.
With rising awareness of data privacy, businesses and platforms alike faced greater pressure to maintain transparency in data handling. Audio-based social platforms and podcasts also gained attention. Emerging decentralized networks started attracting privacy-conscious users, while misinformation and fake content remained ongoing concerns.
Platform-Specific Strategies for Singapore Market
Instagram: Visual Storytelling Excellence Instagram’s algorithm heavily favors video content, with Reels receiving 3x more engagement than static posts in the Singapore market. Local food content, particularly hawker center discoveries and restaurant reviews, consistently performs well.
Winning Content Types: – Behind-the-scenes content from local businesses – User-generated content featuring Singapore landmarks – Educational content about local culture and traditions – Sustainability initiatives and green practices
TikTok: Trend-Driven Discovery TikTok’s “For You” page has become Singapore’s unofficial trend forecaster. Local hashtags like #SingaporeFood, #SGLife, and #LocalBusiness regularly trend, creating opportunities for organic reach.
Growth Strategies: – Participate in local challenges and trends – Create content around Singapore-specific topics – Collaborate with local TikTok creators – Use trending local audio and music
LinkedIn: Professional Networking Hub Singapore’s status as a regional business hub makes LinkedIn crucial for B2B marketing. The platform’s emphasis on professional development and industry insights resonates strongly with Singapore’s career-focused population.
WhatsApp Business: Direct Communication Channel WhatsApp’s role extends beyond messaging to become a comprehensive business tool. Local businesses use it for customer service, order taking, and even conducting virtual shopping sessions.
Business Adoption and Investment
Businesses in Singapore embraced social media in multiple ways in 2025. Social media ad spend rose by 15.9% to US$510 million, while influencer advertising grew by 13.6% to US$106 million. WhatsApp was widely used for direct communication, and Facebook excelled at community-building. The adoption of social commerce became widespread, with TikTok Shop and Instagram Shopping becoming essential sales channels. To strengthen social proof, businesses collaborated more with micro and nano-influencers for authentic testimonials—often through partnerships with an Influencer Marketing Agency familiar with the local ecosystem. Employee stories were used to humanize brands and build trust. Companies also invested in analytics tools to monitor campaign performance and understand audience behaviour.
For companies focusing on inbound and evergreen content strategies, working with a Content Marketing Agency became a critical component of brand building. These agencies help local and regional businesses craft narratives, optimize for search, and maintain consistent, value-driven communication across platforms. Meanwhile, Chinese brands expanding into Singapore—or Singaporean brands targeting Chinese-speaking audiences—found success through a Xiaohongshu Marketing Agency, which specializes in navigating the Little Red Book ecosystem and tapping into Gen Z buying power.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance Singapore’s regulatory framework for social media marketing is comprehensive, with the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) and Advertising Standards Authority of Singapore (ASAS) guidelines governing digital marketing practices.
Key Compliance Areas: – Data Protection: Strict requirements for collecting, storing, and using consumer data from social media campaigns – Advertising Disclosure: Clear labeling requirements for sponsored content and influencer partnerships – Content Standards: Guidelines for culturally sensitive content in Singapore’s multicultural society – Financial Services: Additional regulations for fintech and financial services companies marketing through social media.
Economic Impact and Growth Projections
Social media became increasingly embedded in Singapore’s digital economy. The social commerce sector was expected to grow substantially, with projections reaching US$8.47 billion by 2029. Platforms evolved into full-fledged shopping channels, further blurring the lines between browsing and buying. Media consumption trends were largely influenced by social media, particularly in food and entertainment. Digital advertising continued to rise, with social media accounting for a growing share of ad spend. Despite losing some ground in web traffic referrals, Facebook remained an important driver of online visits.
Future Predictions: What’s Next for Social Media Singapore
1. Augmented Reality (AR) Integration With Singapore’s push toward becoming a “Smart Nation,” AR integration in social media is expected to explode. Local businesses are already experimenting with AR try-on features and virtual showrooms.
Predicted Growth: AR-enabled social media campaigns expected to increase by 400% by 2026.
2. Voice-Activated Social Commerce Singapore’s multilingual population makes voice technology particularly relevant. Platforms are developing voice recognition for local languages and dialects, opening new avenues for content creation and commerce.
3. Blockchain-Based Creator Economy: Singapore’s progressive stance on blockchain technology will likely lead to new monetization models for content creators, including NFTs and cryptocurrency-based reward systems.
4. Enhanced Privacy Controls Following global trends, social media platforms will implement more sophisticated privacy controls, affecting how businesses collect and use customer data for marketing purposes.
This high engagement with social media is closely tied to Singapore’s advanced digital infrastructure, which boasts 95.8% internet penetration (5.61 million users) and 179% mobile penetration (10.5 million connections)—making it one of the world’s most connected nations. Singapore achieved the world’s first nationwide 5G coverage, creating unprecedented opportunities for high-bandwidth social experiences like live streaming, AR filters, and immersive video content. Smart Nation 2.0’s emphasis on digital services and data-driven governance creates new opportunities for using social media in citizen engagement. Singapore’s focus on AI talent aligns well with the increasing use of AI in marketing for personalization and campaign efficiency. The government’s emphasis on cybersecurity and digital trust also supports the responsible handling of social media data. Additionally, digital inclusion goals highlight the need for accessible content catering to all users across Singapore’s 6.11 million population.
For businesses, the insights from 2025’s social media landscape point to several actionable strategies. Establishing a strong presence on platforms such as WhatsApp, Facebook, and TikTok is essential. Tailoring content to suit each platform’s audience, leveraging short-form videos, and collaborating with smaller influencers can boost authenticity and engagement. Businesses should invest in integrated shopping features, build transparent data policies, and stay informed on emerging tech like AI content creation and decentralized networks. Employee stories, private groups, and robust analytics tools can further strengthen brand loyalty and performance. Ultimately, aligning social media strategies with broader national initiatives like Smart Nation and digital transformation efforts will be key to sustained success.
In conclusion, Singapore’s social media environment in 2025 is marked by widespread adoption, platform diversification, and fast-evolving consumer behavior. With the right strategies—and with expert guidance, businesses can leverage this landscape not only for marketing and engagement but also for direct sales and long-term brand building. A data-driven and locally informed approach will help unlock the full potential of social media in one of Asia’s most digitally advanced nations.
The Road Ahead: Preparing for 2026 and Beyond Singapore’s social media landscape will continue evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancement and changing consumer preferences. Success will require adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and a deep understanding of local nuances.
Businesses that invest in understanding Singapore’s unique social media ecosystem, embrace new technologies, and maintain authentic connections with local communities will thrive in this dynamic environment. The key is to remain agile, data-driven, and genuinely committed to serving Singapore’s diverse and digitally sophisticated population.
As we look toward the future, one thing is certain: social media will remain central to Singapore’s digital economy, offering unprecedented opportunities for businesses willing to invest in understanding and engaging with this vibrant market.
Need Expert Guidance for Your Social Media Strategy in Singapore?
Hashmeta combines deep local market knowledge with cutting-edge digital marketing technology to help your brand succeed in Singapore’s dynamic social media landscape. Our team of specialists can develop customized strategies that deliver measurable results across platforms.
From content creation and community management to influencer partnerships and social media marketing optimization, we provide end-to-end solutions tailored to your specific business objectives.
*Latest Trends on Social Media in Singapore (Last updated on October 2025)*
Social Media Platform Mix in Singapore: Nudging the Giants, Not Replacing Them
Singapore remains one of the world’s most digitally saturated markets, with 95.8 % internet penetration and 5.16 million social‑media identities logged at the end of Q2 2025.
Growth is a modest 1.4 % YoY, but time spent keeps climbing: users now average 2 h 28 m daily, spurred by short‑form video and always‑on messaging.
TikTok still leads minutes‑watched, propelled by a wider Asia‑Pacific user base topping 700 million.
Yet platform churn is visible at the margins. Meta’s Threads registered triple‑digit global MAU growth through late‑2024, and local agencies report early‑2025 campaigns reaching ~18 % of Instagram’s Singapore audience—already enough to justify test budgets.
ByteDance counters with lifestyle app Lemon8, whose creator workshops and “photo‑essay” format resonate with fashion‑beauty micro‑influencers.
Meanwhile, Chinese discovery engine Xiaohongshu (RED) is carving a luxury‑travel niche: Marina Bay Sands alone captured nearly half of hotel‑category engagements on the platform in 2024.
The lesson: incumbents stay dominant, but campaign planners must budget 5‑10 % for these fast‑growing peripheral channels to capture incremental reach and insights.
AI‑Native Discovery & Content Creation on Social Media
AI momentum is accelerating as brands lean on GenAI for ideation, localisation and real‑time asset tweaking.
Singapore’s own Model GenAI Governance Framework, sets regional benchmarks for transparency, IP and safety—giving marketers clarity to deploy large‑language‑model (LLM) and diffusion tools inside regulated workflows.
Singapore’s home-grown large language model (LLM), Sea-Lion, is steadily gaining traction, with more than 250,000 downloads so far, bolstered by adoption by large companies such as GoTo Group in Indonesia.
GovTech pilots already generate multilingual explainer videos on‑the‑fly, proving the model’s viability for public‑sector outreach.
Commercially, brands use GenAI to auto‑subtitle TikTok reels and produce hyper‑personalised Instagram Story ads, while predictive vision models choose the thumbnail likely to lift hook rate by 27 % (median uplift seen across five FMCG tests). AI’s role is not just creation but discovery: TikTok’s For You feed now fuses on‑device signals with cloud‑based context to surface local hawker features to users within a 2 km radius, a capability quietly rolled out in Q1 2025. (Internal campaign data, corroborated by client briefs; no public citation available.)
Social Commerce 2.0: From Live Deals to Always‑On Stores
Live‑commerce is shifting from novelty to infrastructure. A March 2025 intelligence report pegs Singapore’s social‑commerce GMV at USD 3.17 billion, up 26.8 % YoY, and forecasts a 15.6 % CAGR through 2030.
Shopee Live drives much of that surge, with its parent company guiding 20‑25 % GMV growth SE‑wide in 2025 and maintaining a 52 % share of regional e‑commerce.
Instagram Reels, now averaging a 1.23 % engagement rate (beating photo posts by 75 %), is Meta’s primary social‑commerce gateway; in‑stream Checkout rolled out to selected SG sellers in April 2025, slashing purchase friction.
On TikTok Shop, the top 200 creators in Singapore collectively host 1 800 live streams a week, with beauty and home‑organisation the best‑converting niches. For 2H 2025 planning, brands should treat live‑commerce as a funnel middle layer: seed demand on FYP/Reels, convert via real‑time flash deals, and retarget cart‑abandoners in WhatsApp Channels.
Messaging Apps = Media Channels
WhatsApp remains the republic’s most‑used app, but Channels—public, one‑to‑many broadcast feeds launched here in late‑2024—turned it into a bona fide media space. Local publishers such as TheSmartLocal amassed >100 k followers within two months by delivering snackable neighbourhood tips.
Telegram is the dark‑horse: Singaporeans spend an average 4.7 hours per month on the platform, second only to Malaysia worldwide, and its penetration hit 30.1 %.
Brands leverage boosted channels and mini‑apps for concierge‑style product drops; early adopters in consumer tech report 5‑to‑1 ROAS compared with Instagram Feed ads, thanks to near‑zero CPMs. Crucially, messaging is where first‑party data capture happens: progressive profiling chat‑flows asking one question per interaction outperform traditional landing pages by 32 % lead‑to‑purchase conversion, according to four 2025 ABM pilots.
*Regulation & Trust: Safety Moves to the Fore*
Singapore’s regulatory landscape has tightened markedly in the past 12 months. IMDA’s Online Safety Code, enforced from mid‑2024, demands that “designated services” filter child‑sexual content, allow user toggles for algorithmic feeds and report quarterly on trust‑and‑safety metrics.
Simultaneously, POFMA remains the government’s blunt instrument against misinformation; activist pushback underscores the fine line brands walk when commenting on civic issues.
For marketers, the upshot is diligence: maintain appeal workflows for takedown requests, use whitelisted fact‑checking partners, and bake correction mechanisms into crisis plans. The new AI Framework further obliges brands to watermark GenAI assets and log training data provenance—best handled by integrating metadata tags directly into DAM systems.
Immersive & Avatar‑Led Experiences
While Meta’s Horizon Worlds has yet to see mass uptake, XR activation budgets are rising. Local studios report that briefs for AR try‑ons and collectible NFTs climbed 42 % YoY. MAGES Studio cites metaverse marketing as a top strategic priority for forward‑leaning Singapore retailers in 2024‑25.
Avatars and generative‑AI faces taking centre‑stage, with virtual influencer collab held up as a template for blending physical retail and social fuzz.
Labels from beauty (Laneige) to luxury (Gucci) now run micro‑immersive pop‑ups where users’ avatars mirror real‑world store visits.
Although reach is niche, dwell‑time exceeds 15 minutes and yields zero‑party intent data—gold for retargeting.
Micro‑Communities & Hyperlocalisation
With mainstream feeds saturated, Singaporeans seek affinity spaces in private groups, hobby‑‑specific channels and language‑layered communities (e.g. dialect‑flavoured Telegram “Kopi Corner” chats). Telegram’s Topic sub‑threads and Discord‑style voice rooms meet this need, while TikTok pushes Communities pilot tabs for interest verticals. Brands that provide utility—exclusive recipes, early sneaker drops, or cashback code swaps—win. But hyperlocal also means hyper‑responsible: under IMDA’s AI governance playbook, micro‑targeting must remain “contextual, not manipulative,” driving a renaissance in consent‑driven, value‑exchange content.
Key Takeaways for the updated 2H 2025 Strategy
- Allocate 70 % of budget to the big four (TikTok, Instagram, Facebook, YouTube) but earmark 10 % for emergent players (Threads, Lemon8, Xiaohongshu) to future‑proof reach.
- Blend AI into every workflow—content, targeting, moderation—while adhering to Singapore’s GenAI framework for provenance and safety.
- Treat live‑commerce as a full‑funnel engine: tease on short‑form video, convert via streams, nurture via WhatsApp/Telegram.
- Prepare compliance playbooks for the Online Safety Code and POFMA to safeguard brand equity.
- Experiment in immersive worlds and avatar collabs to lock in early mover advantages and gather first‑party intent data.






